OOPS - PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT
ANKLE FOOT


See instructions for drawing your pain on devices.
You can draw a pain chart / graph to show how the pain changes over the course of 24 hours.
Then follow the range of movement guide below. It might be useful to have another person to estimate how much of your range you have before you feel pain or stiffness.
Write the percentage of movements in the calculator below and it will give you the average of all ranges as your functional range. This will give you the starting point and link for your rehabilitation as below.
Write this down so you can refer to it every few days to measure your improvement by following the rehabilitation guides as below. Then click the clear button to clear the form for the next time you use.
Also review a Gait / Walking Assessment
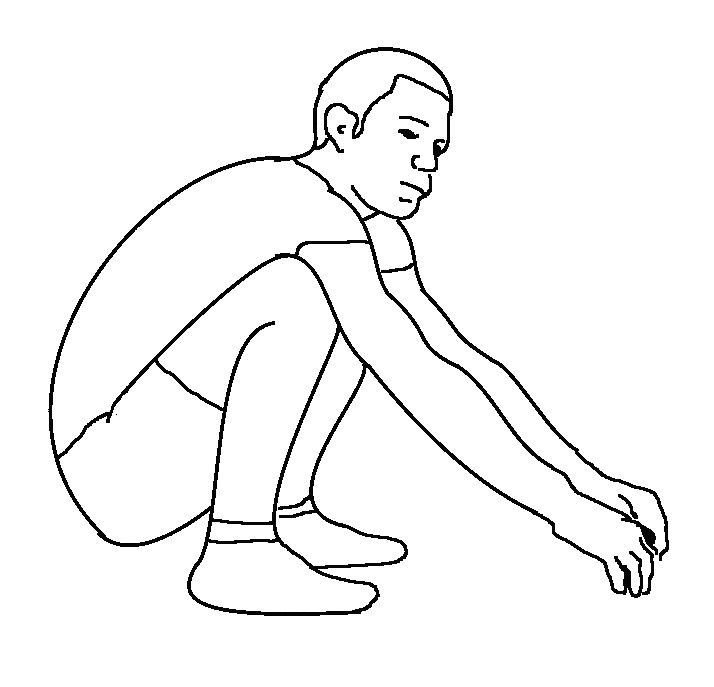
Full squat is the best sign of the full function of legs and low back.
With feet apart and flat on floor, and gently balancing with hands on bench or table, squat until you feel pain.
Full squat (100%) = with feet flat on the floor, sitting freely on the back of your legs.
90% is near full squat with stiffness or pain.
50% = thighs parallel to the floor
Write as Squat = e.g 75%
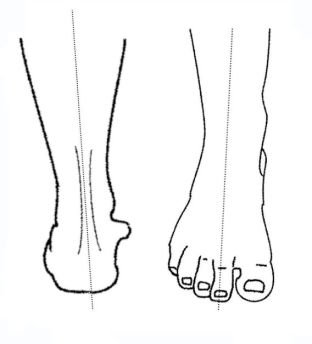

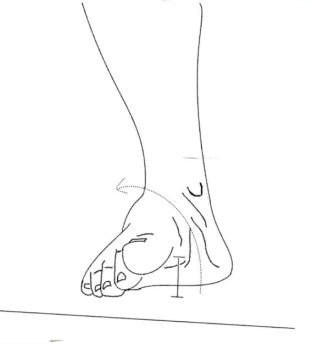
Inversion (Inv)
Guide to commencing your self therapy from the Functional Range
If there is pain in the calf muscle or achilles tendon (above heel), tape the muscle daily until the ankle DF range is better than 70% (without tape) and you can walk without a limp.
Total average range less than 40% start your therapy here.
Total average range between 40 and 70% start your therapy here.
Total average range more than 70% start your therapy here.